
Digital visual interface cables play a vital role in transmitting video signals between devices. These cables ensure high-quality image delivery by supporting both analog and digital formats. You might find them connecting computers to monitors, projectors, or even medical-grade displays. In fact, over 65% of medical displays shipped in 2022 included DVI ports, highlighting their importance in healthcare. Engineers also favor these cables for their resistance to electromagnetic interference, making them reliable in industrial settings. Their continued demand, reflected by $120 million in DVI-to-HDMI adapter sales in 2023, proves their relevance in hybrid connectivity.
DVI cables help connect devices and send clear video signals.
Use DVI-D cables for digital devices and DVI-I for both types.
Pick dual-link DVI cables for sharper pictures and better performance.
Check your device details to pick the correct cable and avoid problems.
Buy cables that work with higher resolutions to prepare for the future.

Digital visual interface cables come in different types, each designed for specific purposes. Understanding these types helps you choose the right cable for your devices.
DVI-D cables transmit only digital signals. These cables are ideal for connecting modern devices like computers and monitors that support digital displays. They ensure high-quality video output without the interference often found in analog signals. If you prioritize sharp and clear visuals, DVI-D is a reliable choice.
DVI-A cables handle analog signals exclusively. These cables work best with older devices, such as legacy monitors or projectors, that rely on analog technology. While they don't offer the same clarity as digital cables, they remain useful for maintaining compatibility with older systems.
Tip: If you’re using older equipment, DVI-A cables can bridge the gap between outdated and newer technologies.
DVI-I cables combine the features of DVI-D and DVI-A. They support both digital and analog signals, making them versatile. You can use them with a wide range of devices, whether they are digital or analog. This flexibility makes DVI-I a popular choice for users who need compatibility across different systems.
Here’s a quick comparison of DVI and VGA, another common interface:
Feature | DVI | VGA |
|---|---|---|
Type | Digital | Analog |
Development Year | 1999 | 1987 |
Usage | Primarily for digital displays | Used for older monitors and projectors |
Quality | Higher quality with digital signals | Lower quality due to analog signals |
Current Relevance | Widely used in modern devices | Being phased out in favor of digital |
This table highlights why digital visual interface cables, especially DVI-D and DVI-I, remain relevant in 2025. They provide better quality and compatibility compared to older analog options like VGA.
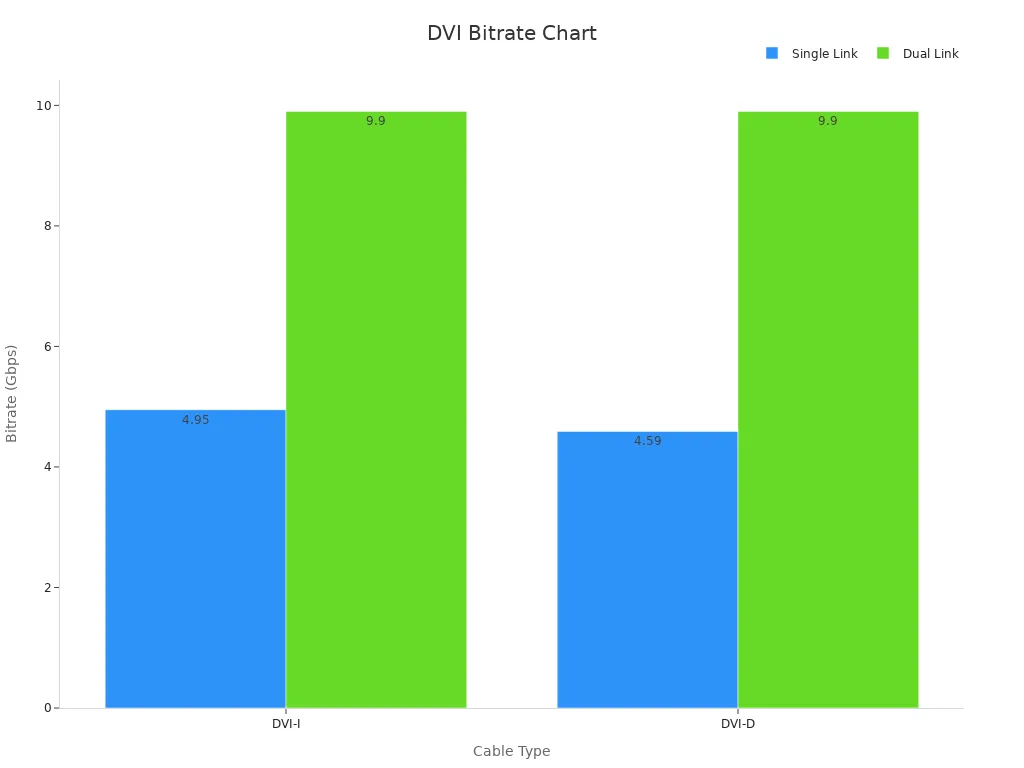
When choosing a DVI cable, you might encounter two options: single-link and dual-link. These terms refer to the number of data channels within the cable, which directly impacts its performance.
Single-link DVI cables use one TMDS (Transition Minimized Differential Signaling) link. This setup supports resolutions up to 1920 × 1080 at 60Hz for DVI-D and 1600 × 1200 at 60Hz for DVI-I. It works well for standard HD displays and general-purpose use. However, if you need higher resolutions or better refresh rates, single-link might not meet your needs.
Dual-link DVI cables, on the other hand, double the data channels. This configuration increases the bitrate and allows for higher resolutions, such as 2048 × 1536 at 60Hz. Dual-link cables are ideal for high-resolution monitors, professional editing, or gaming setups requiring sharper visuals.
Here’s a detailed comparison of single-link and dual-link DVI cables:
DVI-I (Single Link) | DVI-I (Dual Link) |
|---|---|
Bitrate | |
Max. Supported Resolution | 1600 × 1200 @ 60Hz |
DVI-D (Single Link) | DVI-D (Dual Link) |
|---|---|
Bitrate | 4.59 Gbps |
Max. Supported Resolution | 1920 × 1080 @ 60Hz |
Tip: If you’re working with a 4K monitor or a display requiring ultra-high resolution, consider upgrading to a dual-link DVI cable. It ensures smoother performance and better image quality.
Understanding the difference between single-link and dual-link DVI cables helps you make informed decisions. Whether you need a cable for everyday tasks or high-performance applications, knowing these distinctions ensures you choose the right one for your setup.
Digital visual interface cables are highly effective for connecting computers to monitors. They deliver high-quality digital video signals, ensuring clear and precise image quality. This makes them ideal for modern digital displays, whether you're working in a home office or a multimedia environment. DVI cables were developed as a successor to VGA, offering support for both digital and analog signals. For example, DVI-I cables are compatible with VGA, while DVI-D focuses solely on digital signals. This versatility allows you to use them with a wide range of devices, making them a reliable choice for contemporary setups.
If you're a gamer or someone who works with high-resolution displays, digital visual interface cables can enhance your experience. These cables support resolutions and refresh rates that are essential for smooth and immersive visuals. While HDMI 2.1 offers a bandwidth of 48 Gbps and supports resolutions up to 10K, DVI cables remain a solid option for gaming setups that don't require such extreme specifications. For high-performance displays, DisplayPort 1.4 supports 4K at 120Hz, but DVI cables still hold their ground for many users due to their reliability and compatibility with older systems. Whether you're gaming or editing videos, these cables can provide the performance you need.
Older devices and legacy systems often rely on digital visual interface cables for connectivity. Many older monitors and projectors use analog signals, which DVI-A cables can handle effectively. If you have a mix of old and new devices, DVI-I cables offer a practical solution by supporting both digital and analog signals. This makes them a valuable tool for bridging the gap between outdated technology and modern equipment. For example, if you're using a legacy projector in a classroom or office, a DVI cable can ensure compatibility and maintain functionality.
Digital visual interface cables offer several benefits, making them a reliable choice for many users. These cables transmit digital signals, ensuring superior image quality compared to analog options like VGA. You’ll notice sharper visuals and more accurate colors, especially in high-definition displays. This makes DVI cables ideal for professional environments such as graphic design studios, where image clarity is crucial.
Users also appreciate the durability of DVI cables. They are built to last and maintain signal integrity over longer distances. Unlike VGA, which suffers from signal degradation, DVI ensures consistent performance. For example, transitioning to DVI has helped streamline workflows in industries that rely on high-quality displays.
Here’s a quick comparison of DVI and VGA to highlight the advantages:
Metric | DVI | VGA |
|---|---|---|
Signal Type | Digital | Analog |
Image Quality | Superior, especially in HD | Adequate for standard use |
Signal Integrity | High, less prone to loss | Deteriorates over distance |
Maximum Resolution | Up to 4K | Limited by analog capabilities |
Durability | High | Moderate |
Note: If you work with high-resolution monitors or professional displays, DVI cables can significantly enhance your experience.
Despite their advantages, DVI cables have limitations that you should consider. They struggle to support resolutions beyond 2560×1600 at 60 Hz, making them less suitable for ultra-high-definition displays. Emerging technologies like HDMI 2.1 and DisplayPort 2.0 now support 8K resolutions, leaving DVI behind in terms of performance.
DVI cables also lack modern features such as dynamic HDR and adaptive sync, which are essential for gaming and multimedia applications. Additionally, they consume more power compared to newer standards. Retrofitting older systems with DVI can be costly, with expenses exceeding $10,000 per unit in some cases.
Here’s a comparison of DVI and emerging technologies:
Limitation Type | DVI Details | Emerging Technologies (HDMI, DisplayPort) |
|---|---|---|
Bandwidth Constraints | HDMI 2.1 and DisplayPort 2.0 support 8K at 60 Hz. | |
Feature Support | Lacks modern features like dynamic HDR and adaptive sync. | HDMI and USB-C integrate power delivery, audio, and data. |
Cost of Transition | Retrofitting legacy systems can exceed $10,000 per unit. | HDMI and DisplayPort cables are up to 40% cheaper. |
Energy Efficiency | DVI consumes more power compared to modern standards. | HDMI 2.1 consumes up to 30% less power for identical tasks. |
Market Adoption | Only 12% of new desktop monitors included DVI ports in 2022. | Newer devices prioritize HDMI and USB-C for universal compatibility. |
Tip: If you’re upgrading your setup, consider whether DVI meets your needs or if newer interfaces like HDMI or DisplayPort would be a better fit.

When comparing digital visual interface cables to HDMI, you’ll notice key differences in functionality and performance. HDMI supports both video and audio transmission, while DVI is limited to video only. This makes HDMI more versatile for home entertainment systems and gaming setups. HDMI also offers higher bandwidth, with HDMI 2.1 reaching up to 48 Gbps, compared to DVI’s maximum of 7.92 Gbps for dual-link cables. This allows HDMI to handle resolutions up to 8K at 60Hz or 4K at 120Hz, whereas DVI struggles with resolutions beyond 2560×1600 at 60Hz.
For gaming, HDMI includes features like Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) and Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), which enhance performance. DVI, however, remains a reliable choice for professional environments where high-quality video output is essential. If you need a cable for modern devices, HDMI is the better option due to its advanced features and widespread compatibility.
DVI and VGA differ significantly in terms of technology and performance. VGA transmits analog signals, while DVI supports digital signals, resulting in sharper and clearer visuals. This makes DVI a better choice for high-definition displays. VGA, developed in 1987, is now considered outdated and is being phased out in favor of digital interfaces like DVI and HDMI.
DVI also offers higher resolutions and better signal integrity over longer distances. For example, DVI can support resolutions up to 2560×1600, while VGA struggles with anything beyond 1920×1080. If you’re using older monitors or projectors, VGA might still be necessary. However, for modern setups, DVI provides superior performance and compatibility.
DisplayPort outperforms DVI in almost every aspect. It supports higher resolutions and refresh rates, making it ideal for gaming and professional use. DisplayPort 1.4, for instance, handles 4K at 120Hz and even 8K at 60Hz, while DVI is limited to 2560×1600 at 60Hz. DisplayPort also allows daisy-chaining, enabling you to connect multiple monitors with a single cable.
In terms of market trends, DisplayPort is gaining popularity in gaming and high-end professional environments. DVI, on the other hand, is primarily used in legacy systems. If you’re upgrading your setup, DisplayPort offers better performance and more features, making it a future-proof choice.
Here’s a quick comparison of these interfaces:
Cable Type | Performance | Market Trends |
|---|---|---|
HDMI | High-definition video and audio, supports 8K at 60Hz and 4K at 120Hz | Most prevalent in consumer electronics, continuous advancements drive demand |
DisplayPort | Superior performance with higher resolutions and refresh rates, daisy-chaining | Popular in gaming and professional environments, especially with high-end monitors |
DVI | Digital signal transmission, used in legacy systems | Less common, but still relevant for older devices |
Tip: If you’re deciding between these interfaces, consider your device compatibility and performance needs. For modern setups, HDMI or DisplayPort will likely serve you better than DVI.
Selecting the right digital visual interface cable depends on your specific needs. Start by identifying the type of devices you want to connect. For example, if you are using a modern monitor, a DVI-D cable might be the best choice for its digital signal support. On the other hand, older devices may require DVI-A or DVI-I cables for compatibility with analog signals.
Resolution and refresh rate requirements also play a crucial role. If you need to display high-resolution images or videos, a dual-link DVI cable is better suited for the task. Single-link cables work well for standard HD displays but may not meet the demands of professional editing or gaming setups.
Cable length is another factor to consider. Longer cables can lead to signal degradation, especially with analog signals. For distances over 15 feet, look for cables with built-in signal boosters or consider alternative interfaces like HDMI or DisplayPort.
Tip: Always check the ports on your devices before purchasing a cable. This ensures you choose the correct type and avoid unnecessary adapters.
As technology evolves, ensuring compatibility with digital visual interface cables requires careful planning. First, verify the specifications of your devices. Many modern monitors and GPUs still support DVI, but newer models may prioritize HDMI or DisplayPort. Check the user manuals or product descriptions for supported interfaces.
Adapters can help bridge the gap between older and newer devices. For instance, a DVI-to-HDMI adapter allows you to connect a DVI cable to an HDMI port. However, keep in mind that adapters may not support advanced features like HDR or high refresh rates.
Future-proofing your setup is also important. If you plan to upgrade your devices soon, consider investing in cables that support higher resolutions and refresh rates. This ensures your cables remain useful even as your technology changes.
Note: Compatibility issues often arise from mismatched resolutions or refresh rates. Adjust your device settings to match the capabilities of your cable for optimal performance.
Digital visual interface cables continue to play a vital role in connecting devices in 2025. They ensure high-quality video transmission for various applications, including computer monitors, projectors, and even some HDTVs. Their ability to support both digital and analog signals makes them versatile and reliable for legacy systems and modern setups alike.
Application | Description |
|---|---|
Computer Monitors | DVI is commonly used to connect video sources to computer monitors, ensuring high-quality video transmission. |
Projectors | DVI technology is utilized to transmit high-definition video signals from computers to projectors. |
HDTVs and DVD Players | Some HDTVs and DVD players are equipped with DVI inputs, allowing for high-quality digital video reception. |
While newer technologies like HDMI and DisplayPort dominate the market, digital visual interface cables remain relevant for specific use cases. Their durability and compatibility with older devices ensure they still have a place in today’s tech landscape.
DVI-D cables transmit only digital signals, making them ideal for modern devices. DVI-I cables, however, support both digital and analog signals. This versatility allows you to connect to a wider range of devices, including older monitors that rely on analog technology.
No, DVI cables cannot support 4K resolution. The maximum resolution for dual-link DVI cables is 2560×1600 at 60Hz. For 4K displays, you should consider using HDMI 2.0 or DisplayPort 1.4, which are designed for higher resolutions and refresh rates.
Yes, DVI cables remain relevant for specific use cases. They are commonly used in legacy systems, older monitors, and professional environments requiring high-quality video output. However, newer interfaces like HDMI and DisplayPort are more prevalent in modern devices.
Choose single-link DVI cables for standard HD displays with resolutions up to 1920×1080. Opt for dual-link DVI cables if you need higher resolutions, such as 2560×1600, or better refresh rates. Dual-link cables provide more bandwidth, making them suitable for professional and gaming setups.
Yes, you can use adapters to connect DVI cables to other interfaces like HDMI or VGA. For example, a DVI-to-HDMI adapter allows you to connect a DVI cable to an HDMI port. However, adapters may not support advanced features like HDR or high refresh rates.
Tip: Always check your device's specifications before purchasing an adapter to ensure compatibility.